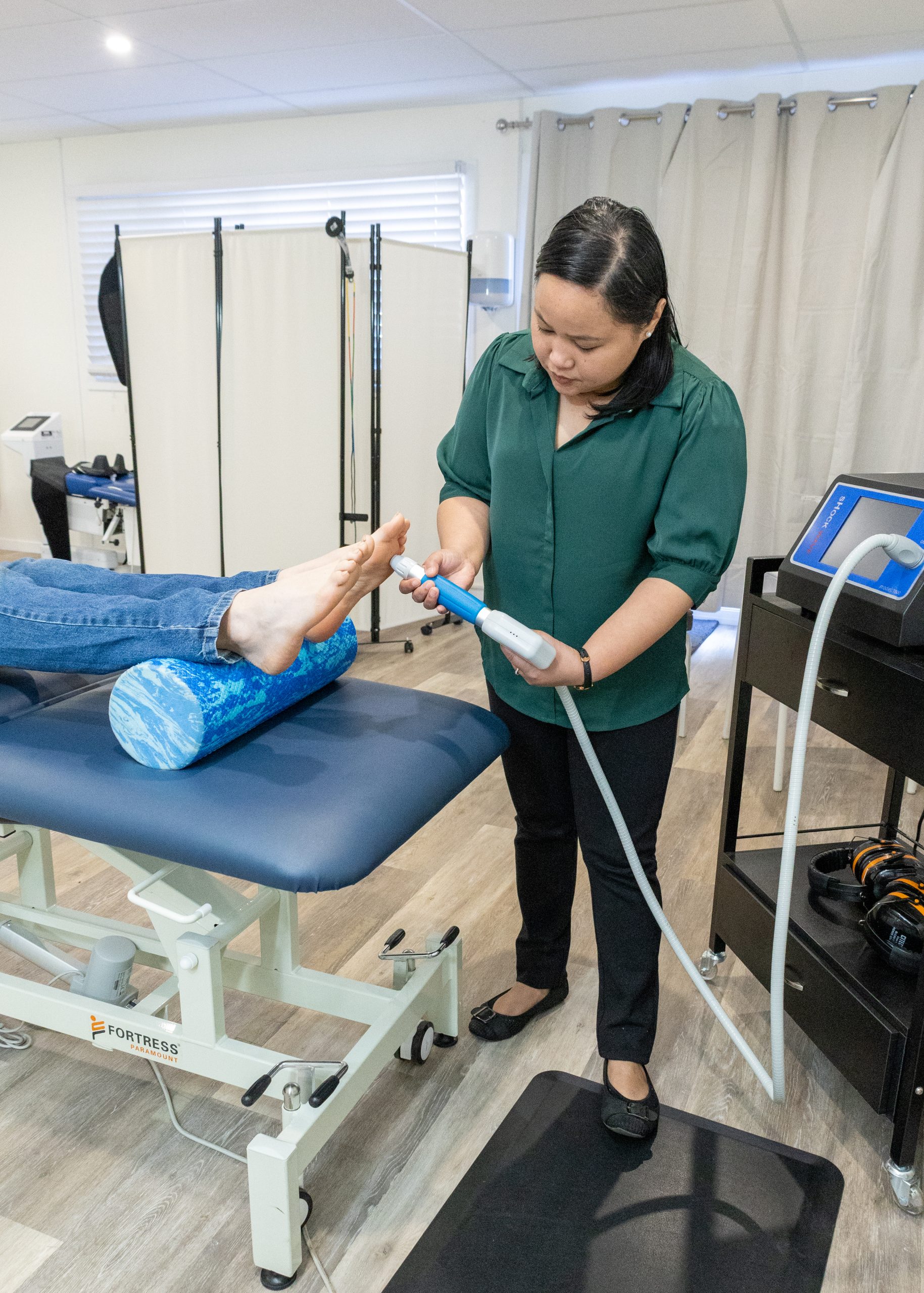
Shockwave Therapy
Evidence-based care for chronic muscle, tendon and joint pain
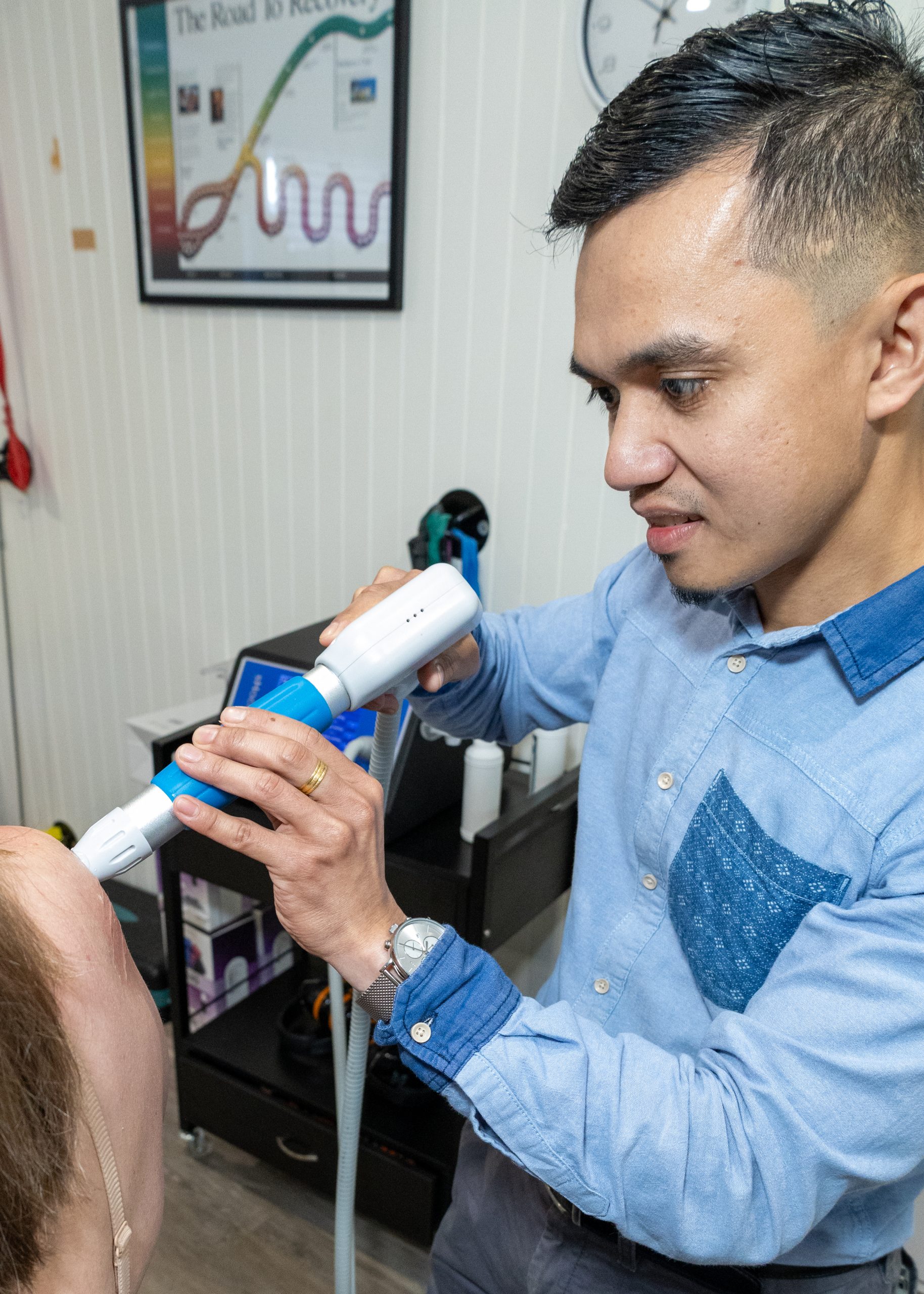
At Kingaroy Chiropractic & Wellness, we use Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT) as part of our advanced musculoskeletal treatment options. Shockwave therapy is widely recognised in sports medicine and rehabilitation for its effectiveness in treating stubborn and chronic conditions that have not responded to standard treatment approaches.
What Is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave Therapy uses high-energy acoustic pressure waves to stimulate healing in damaged tissues. These pressure waves:
Increase local blood flow
Break down calcification and scar tissue
Reduce chronic inflammation
Disrupt pain signalling pathways
Stimulate collagen production and tissue regeneration
Multiple randomised controlled trials and systematic reviews support shockwave therapy as a safe, non-invasive, and clinically effective treatment for many chronic soft-tissue disorders.
Conditions Supported by Research
Plantar Fasciitis / Heel Pain
Shockwave therapy has strong evidence for chronic plantar fasciitis, with multiple studies showing significant pain reduction and improved function. ESWT is also recommended when symptoms have persisted for more than six weeks.
Shoulder Tendinopathies (Including Calcific Tendinitis)
Studies show improved range of motion, decreased pain, and faster resorption of calcium deposits compared to standard physiotherapy alone.
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Shockwave has been shown to reduce pain and improve elbow function—particularly when combined with exercise and manual therapy.
Achilles Tendinopathy & Patellar Tendinopathy
Research supports ESWT as an effective option for patients who have failed conservative management such as rest, stretching, orthotics, and manual therapy.
Other conditions with growing evidence include:
Trochanteric (hip) tendinopathy
Hamstring tendinopathy
ITB syndrome
Medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints)
What to Expect During Treatment
Assessment – Your clinician evaluates whether shockwave is indicated.
Application – Gel is applied and the handheld device delivers pulses over the affected area for 3–8 minutes.
Rehabilitation Plan – Patients may benefit from combining shockwave with chiropractic care, Physiotherapy, soft-tissue therapy, load management, and corrective exercise.
Depending on the circumstances many people feel improvement within 1–3 sessions, with optimal results occurring over 3–6 sessions.
Is Shockwave Therapy Painful?
You may feel a short, sharp sensation when the wave targets a painful structure. This discomfort typically decreases during treatment and is a sign that the therapy is stimulating the affected tissue. Most patients describe it as intense but tolerable.
References
Al Abadi, H., Cetti, R., Gkogkas, G., & Henriksen, M. (2023). Effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Foot & Ankle International, 44(4), 411–424.
Buchbinder, R., Ptasznik, R., Gordon, J., Buchanan, J., Prabaharan, V., & Forbes, A. (2002). Ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 288(11), 1364–1372.
Cheing, G. L., Chang, H., Lo, S. K., & Wan, J. W. (2020). Effects of shockwave therapy on chronic lateral epicondylitis: A randomized double-blind study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 99(6), 520–527.
Gerdesmeyer, L., Frey, C., Vester, J., Maier, M., & Weil, L. (2008). Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy is safe and effective in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 36(11), 2100–2109.
Ioppolo, F., Tattoli, M., Di Sante, L., et al. (2013). Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for Achilles tendinopathy. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 92(4), 337–343.
Loew, M., Daecke, W., Kusnierczak, D., & Seil, R. (1999). Shock-wave therapy is effective for chronic calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (British Volume), 81(5), 863–867.
Rompe, J. D., Furia, J. P., & Maffulli, N. (2009). Eccentric loading vs. shock wave treatment for chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy: A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 37(3), 463–470.
Speed, C. (2014). A systematic review of shockwave therapy in tendinopathies. BMJ Open, 4(6), e002528.